Printed from acutecaretesting.org
May 2000
Clinical cases on detection of critical limb ischemia
Please click on the links to read the cases.
- Thomas K. Hunt - Investigating chronic foot wounds
- Raj Mani - Management of venous ulcers
- Dirk Th. Ubbink - Detecting critical limb ischemia
- Henri Bounameaux - Determining amputation level
- Caroline E. Fife - Surgical inverventions - Patient selection and prediction of wound healing
- Andreas Scheffler - Assessment of peripheral arterial occlusive disease
Case 1 - Investigating chronic foot wounds
Tissue hypoxia is the most frequent, proximate cause of failure to heal. The most direct assessment is to measure transcutaneous pO2 (tcpO2). When done in conjunction with arterial oxygen tension, tcpO2 becomes more powerful because then the distinction between hypoxia due to vascular disease and hypoxia due to lung and heart diseases can be made. The tcpO2 response to oxygen breathing is the best known way to assess peripheral perfusion. When regional tcpO2 is measured in the vascular zones of the foot, distal obstruction can be inferred from the differences between the tcpO2 values and from the location of the ulcer.
Clinical case
An 80-year-old woman suffered from a chronic, painful
ulcer necrosis of the distal toes of one foot. There was no
evidence of infection. There was no hair on the affected foot,
which was cold and cyanotic. The skin was atrophic. No pulses were
present, and this was confirmed with Doppler sonography. An
arteriogram had been done at another institution, where the woman
had been offered an amputation but she had declined all treatment
options.
Transcutaneous oxygen measurements performed in the area of cyanosis revealed an unexpectedly high value, 35 mmHg, and a significant response to oxygen breathing. When the electrode was removed, the nurse noted a transient pinkish spot where it had been. The patient’s foot became pinker after immersion in warm water. This led us to a diagnosis of vasospastic disease. She continued to decline all therapy, but after considerable discussion, she agreed to a sympathetic neurolysis with injected alcohol and continuous warmth with a fur-lined boot. tcpO2 and its response to oxygen breathing improved immediately after the neurolysis (see diagram below). The pain disappeared by the next week. Within approx. four months, the necrotic distal toes separated, revealing full epithelization beneath. The foot remains cyanotic whenever it is removed from the boot, but the patient reports no pain.
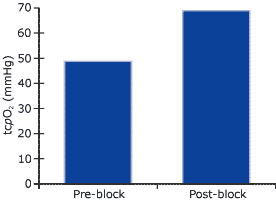
This case illustrates a circumstance in which only the measurement of oxygen can tell the full story. Although the patient did have significant arterial disease, it was not sufficient to cause the necrosis. Vasospastic disorders often occur in conjunction with pain due to arterial disease.
Only the measurement of oxygen can tell the full story.
Author
Thomas K. Hunt
Department of Surgery
University of California
San Francisco
USA
Case 2 - Management of venous ulcers
Once the etiology of a chronic wound such as a venous ulcer is determined, the therapeutic options for management essentially comprise suitable dressings and compression bandages. It is more difficult to deal with the reasons of the chronicity which range from edema to infection. tcpO2 measurements at 43-45 °C permit changes which are associated with healing to be reliably detected [1]. Low values of tcpO2 around non-healing wounds also indicate the need to reconsider therapeutic options.
Clinical case
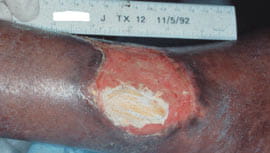
A 78-year-old woman suffered from intractable ulcers
and grossly edematous legs. She had a large ulcer (> 75
cm2) in the region of the medial malleolus, which had
failed to heal for 20 years. As her husband was dependent on her,
she was reluctant to be hospitalized for any length of time. It was
decided that she would be admitted for bed rest with leg elevation
for 24 hours.
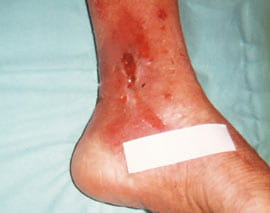 |
tcpO2 was measured on the superior edge of a venous ulcer. Patient was supine at the time. Control values may be derived from measurements on the chest or on the ipsilateral forearm. |
On admission, pulses were barely palpable because of swelling. ABI was > 0.7. tcpO2 at 43 °C on the superior edge of the ulcer was 11 mmHg. After 24 hours of leg elevation, her legs had been reduced significantly in size, the ulcer was drier, and tcpO2 had increased to 19 mmHg. After another 24 hours, she was discharged with heavy compression bandages and transferred to the care of community nurses who continued to bandage her legs and persuaded her to comply with the recommended afternoon bed rest with elevation. On healed skin, the tcpO2 value was 31 mmHg.
References
- Pekenmaki K, Kolari PJ and Kiistala U. Intermittent pneumatic compression for the treatment of post-thrombotic ulcers. Clinical and Experimental Dermatology 1987; 12: 350-53.
Author
Raj Mani
Department of Medical Physics and
Medical Engineering
Southampton General Hospital
Southampton
UK
Case 3 - Detecting critical limb ischemia
In a patient presenting symptoms of peripheral vascular insufficiency, the assessment of the severity of the disease and of the need for invasive intervention (surgery or PTA) is usually made on the basis of a patient’s clinical status and peripheral blood pressure parameters. Transcutaneous oxygen measurements (tcpO2) yield information about local skin microcirculation. Disturbed microcirculation is the ultimate cause of tissue loss. Hence, this technique is an excellent additional diagnostic tool, especially when the clinical symptoms are atypical or when diabetes, which can cause critical leg ischemia to exist without severely reduced ankle pressure, is present. It is easy to use and can be applied even after amputation of a toe, which prevents toe pressure measurements. Furthermore, tcpO2 measurements are useful for predicting the need for an imminent amputation and for assessing the wound healing potential in these patients.
Clinical case
A 65-year-old woman suffered from a painless ulcer on
the fifth toe. The ulcer had started as a blister 6 weeks earlier.
She also suffered from mild claudication. She had had type II
diabetes for 32 years, and had been insulin dependent for 20 years.
Other risk factors present were hypertension and hyperlipidaemia.
Medication: Atenolol, Nifedipine, Atorvastatine, and
Losartan/hydrochlorthiazide.
Physical examination showed a warm, reddish foot with a dry, peeling skin and an indolent, probably pressure-induced ulcer on the lateral side of the fifth toe, surrounded by erythema. No arterial ankle pulsations were palpable. Skin sensibility was reduced due to diabetic neuropathy.
The highest ankle Doppler blood pressure was 81 mmHg (ankle/brachial index [ABI]: 55 %), the systolic pressure of the left hallux was 32 mmHg. tcpO2, as measured distally on the dorsum of the foot, was 5 mmHg. Subsequently, duplex ultrasound investigation of the aortoiliac tract showed no significant stenoses, whereas in the left common femoral artery a stenosis with a diameter reduction of more than 50 % was detected. Duplex scanning of the crural arteries showed an occlusion of the proximal anterior tibial artery, the dorsal pedal and the peroneal arteries. Only the posterior tibial artery was patent, albeit with several wall irregularities.
Although the ankle and the toe blood pressures were above the criteria for critical limb ischemia requiring invasive therapy (50 and 30 mmHg, respectively), the low tcpO2 indicated a threatened skin perfusion and a poor wound healing power. Hence, a percutaneous angioplasty of the common femoral artery was performed successfully. ABI was now 71 %, the toe pressure was 37 mmHg, and the tcpO2 was 33 mmHg.
One month later the tcpO2 had decreased to 7 mmHg, while the ABI and toe pressure were 51 % and 36 mmHg, respectively. Thus, an additional angioplasty of the distal popliteal and peroneal arteries was performed, yielding an ankle pressure of 123 mmHg (ABI: 78 %), and a toe pressure of 50 mmHg. tcpO2 also increased, but reached only 25 mmHg (in our clinic a value less than 30 mmHg is regarded as an indication of critical ischemia).
After a fortnight, the fifth toe had to be amputated because of poor wound healing. After another two weeks, the amputation wound was clean and healing. Ankle pressure was 120 mmHg (ABI: 79 %), toe pressure 42 mmHg and tcpO2 41 mmHg. At the three-month follow-up visit the patient had a completely healed wound without complaints.
Ankle and toe pressures were now 129 and 55 mmHg, respectively (ABI: 100 %) and the tcpO2 was 54 mmHg. Half a year later the patient’s condition was unchanged.
In summary, the treatment of this patient’s ischemic ulcer was guided mainly by the tcpO2 findings, since the ankle pressure was probably affected by the presence of media sclerosis due to the diabetes, while the toe pressures were low, but not critically decreased. One can imagine that if the tcpO2 technique had not been applied as an additional tool to assess the presence of critical ischemia, there would have been a considerable risk that the treatment would have been delayed. Progression of the ischemia would then have resulted in extended tissue loss and/or an infection, which would have required more extensive surgery.
This patient’s ischemic ulcer was guided mainly by the tcpO2 findings, since the ankle pressure was probably affected by the presence of media sclerosis due to the diabetes.
Author
Th. Dirk Th. Ubbink
Academic Medical Centre
Department of Vascular Surgery
Amsterdam
The Netherlands
Case 4 - Determining amputation level
In selecting the optimal amputation level, the clinician must balance the necessity for primary wound healing against the need for retaining the maximum limb length. Indeed, the longer the limb is, the better the rehabilitation rate will be; and conversely, the more distal the amputation is, the greater the risk of wound healing failure will be. With clinical criteria, the typical failure rate of below-knee amputation ranges between 10 and 50 %, but the failure rate of too proximal amputations is ill-defined. On the other hand, a systematic literature analysis suggests that a transcutaneous pO2 measurement of 20 mmHg or more at the site of amputation predicts healing with 80 % accuracy [1].
Clinical case
A 78-year-old man was admitted because of a chronic
ulcer on his left foot. He had had the ulcer for more than 6 weeks,
and there was no sign of improvement. Radiological examination
showed osteitis of the fifth metatarsus. The patient had undergone
amputation of the left great toe two years before due to an
infected foot ulcer.
In his previous history, the following relevant events had been recorded:
- diabetes type II for more than 20 years, treated with insulin for the last 7 years
- coronary heart disease with CABG six years ago
- bilateral, invalidating intermittent claudication, leading to left femoropopliteal bypass five years ago and right femoropopliteal bypass four years ago
- cerebrovascular accident (regressive stroke) four years ago
- beside diabetes, cardiovascular risk factors included smoking (stopped 12 years ago), arterial hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia. Patient was on insulin, enalapril, simvastatine and low-dose aspirin.
Six weeks prior to the admission mentioned above, the patient had been treated for a foot ulcer and infectious cellulitis of the foot dorsum. The latter condition responded to antibiotic treatment, but the ulcer did not heal.
The therapeutic options
Because of the absence of wound healing and the
persistent osteitis, amputation was considered the reasonable
therapeutic option. One orthopedic surgeon suggested below-knee
amputation while his colleague favored a more distal,
transmetatarsal level. The first option would surely have been
associated with a 25-50 % risk of ending in a wheelchair for this
elderly patient, who was living alone.
Diabetic neuropathy was present, and pulses were not palpable below the knee. Ankle-brachial systolic pressure index was 1.6 (left) and 1.9 (right), suggesting vessel wall calcifications. Previous great toe amputation precluded systolic pressure measurement at this level. Arteriography disclosed an occluded left femoropopliteal bypass without the possibility of surgical repair due to poor runoff. Transcutaneous pO2 was measured on foot dorsum, calf and thigh levels to help us determine the amputation level. The values were 23, 42, and 51 mmHg, respectively.
The therapeutic choice
Because tcpO2 was above 20 mmHg
in spite of local edema which is known to reduce capillary density
and consequently tissue oxygenation, ischemia was not considered
the primary cause of the ulcer. Amputation level had to be decided
according to other criteria. Accordingly, the more conservative
option of transmetatarsal amputation was recommended.
Transcutaneous pO2 was measured on foot dorsum, calf and thigh levels to help us determine the amputation level.
References
- Wütschert, R.; Bounameaux, H.: “Determination of amputation level in ischemic limb: re-appraisal of the measurement of transcutaneous oxygen tension”. Diabetes Care 1997; 20: 1315-18.
Author
Henri Bounameaux
Division of Angiology and Hemostasis
University Hospitals of Geneva
Geneva
Switzerland
Case 5 - Surgical inverventions, Patient selection and prediction of wound healing
Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) is associated with high morbidity and mortality, and annually it accounts for about 280 lower limb amputations per million U.S. diabetics. With non-diabetic patients, a history of tobacco abuse contributes to the development of PVD, which often results in critical limb ischemia. Non-invasive vascular tests like arterial Dopplers can provide an ankle/brachial index (ABI), which may be useful in diagnosing a severe disease. However, with patients with calcific vascular disease, ABIs are less reliable than transcutaneous oxygen measurements in screening for critical stenosis. With patients with limb threatening wounds, transcutaneous oxygen measurements can be used to select patients in need of vascular intervention, and to predict wound healing and success after intervention [1].
Clinical case
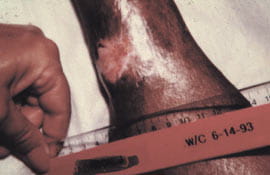
A 54-year-old black woman suffered from ischemic rest
pain and a necrotic lesion on the right lateral ankle. After
débridement of the necrotic eschar, a tendon was found to be
exposed.
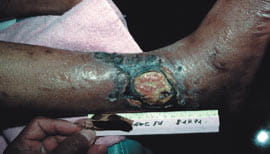 |
Medical history
- Coronary artery disease with angina
- Hypertension
- Lower extremity rest pain
- 30-year smoking history
- Necrotic right lower extremity ulceration
- Recent bilateral aortofemoral bypass
Investigations
Initial transcutaneous oxygen measurements showed 2
mmHg values adjacent to the wound. Non-invasive arterial Dopplers
were performed which revealed an ABI of 0.2. Angiograms revealed
several areas of multifocal vascular disease, particularly of
vessels below the knee.
Therapeutic options
Due to the exposed tendon and wound ischemia, skin grafting was not
an option for wound treatment, nor was extensive plastic surgery
due to inadequate vascular supply. Revascularization was clearly
necessary, but the patient had already undergone surgical
revascularization and declined further surgical intervention.
The therapeutic choice
Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty was performed
on multiple occlusions with restoration of flow to vessels below
the knee. Post procedure transcutaneous oxygen measurements
improved to 46 mmHg. Because of the exposed tendon, the patient
underwent 34 hyperbaric oxygen therapy treatments. Granulation
tissue formed over the tendon and resulted in complete
epithelialization. At the one-year follow-up, the patient had no
recurrence of either ulceration or ischemic pain.
|
|
With patients with calcific vascular disease, ABIs are less reliable than transcutaneous oxygen measurements in screening for critical stenosis
References
- Hanna GP, Fujise K, Kjellgren O, Feld S. Fife C, Schroth G, Clanton T, Anderson V, Smalling R. Infrapopliteal interventions for limb salvage in diabetic patients: importance of aggressive interventional approach and role of transcutaneous oximetry. J Am Coll Cardiol 1997; 30: 664-69.
Author
Caroline E. Fife
Anesthesia
University of Texas Health Science Center
Director, Hermann Center for Wound Healing
Houston
USA
Case 6 - Assessment of peripheral arterial occlusive disease
tcpO2 serves as a noninvasive measure of microvascular skin perfusion in patients with peripheral arterial occlusive disease (PAOD). Because similiar variations of low, medium, and high perfusion pressures correspond with large, moderate, and small changes of tcpO2, respectively, values measured in healthy controls on asymptomatic patients and claudicants widely overlap. In contrast, severe PAOD reduces tcpO2 substantially. Lower limb tcpO2 values in adults normally exceed 40 mmHg in supine and 45 mmHg in dependent leg position.
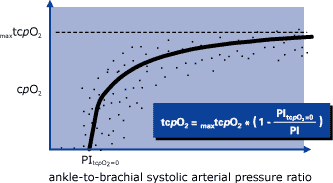
Schematic drawing of the tcpO2 vs. flow circulatory hyperbola. The curve was fitted to original measurements obtained in PAOD patients at an electrode core temperature of 44 °C.
In patients with chronic ischemic rest pain or skin ulcerations, the method provides valuable diagnostic and prognostic information in addition to clinical findings and conventional hemodynamic techniques. To evaluate chronic critical limb ischemia tcpO2 measurements should be obtained in supine as well as dependent leg positions. Poor prognosis with regard to conservative treatment or amputation wound healing is typically associated with tcpO2 values below 10 and 45 mmHg in the horizontal and dependent leg positions, respectively. Because there may be considerable variation in forefoot tcpO2 measured on adjacent skin areas, the simultaneous usage of several electrodes offers the opportunity of detecting “islands of ischemia” more reliably.
Clinical case
A 64-year-old man suffered from nocturnal rest pain
in the left foot for more than two months. Major cardiovascular
risk factors were cigarette smoking, dyslipoproteinemia, and
arterial hypertension. Neither myocardial infarction nor
cerebrovascular events had occured so far. A peripheral arterial
occlusive disease had been diagnosed ten years ago. Since that time
angioplasties of pelvine and superficial femoral arteries were
performed in either leg. A left femoral crural bypass graft, which
was implanted due to acute ischemia two years ago, occluded a few
months ago and all attempts of graft reconstruction failed.
On admission, clinical examination showed palpable pulses at the groin but not at the knee or ankle. Bruits were not found. Inspection of the foot and interdigital spaces excluded skin lesions. Sensoric and motoric functions of the toes were slightly diminished.
Conventional hemodynamic laboratory evaluation was difficult because no Doppler signal was found for noninvasive pressure measurement at neither the ankle nor the dorsum of the foot. Mechanical oscillography revealed missing oscillations at the distal calf even at the lowest external pressure levels of 60 mmHg suggesting critical limb ischemia. Careful color-coded duplex sonography and intra-arterial angiography of the left leg arteries excluded any possibility of further catheder interventions or surgical reconstructions due to long proximal occlusions and multiple calf artery obstructions.
To assess the state of the forefoot skin microvascular blood supply, transcutaneous oxygen measurements were performed in supine and dependent leg position. Although supine tcpO2 values were below 10 mmHg (i.e. suggesting critical limb ischemia), they increased up to the lower normal range in response to limb lowering. This finding is not typical for critical limb ischemia and thus supported the clinical decision to attempt a four-week iloprost infusion therapy (1 ng•kg-1min-1 over 6 hrs daily) accompanied by high doses of analgesics. At the end of this period, the patient’s condition had significantly improved and he could be discharged without persistent nocturnal rest pain.
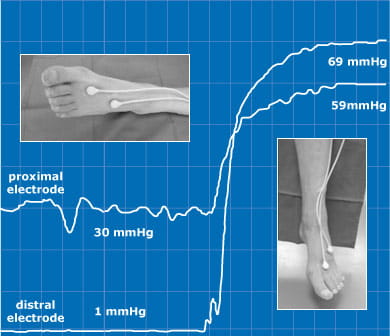
Original tcpO2 recording at the forefoot in supine and dependent leg position. Note the remarkable tcpO2 increase of the distal electrode signal from 1 to 69 mmHg in response to the positional maneuver.
This case demonstrates that tcpO2 can be used even in circumstances where conventional hemodynamic evaluation is not feasible (e.g. missing Doppler flow signal – as was the case here, diabetic media sclerosis, etc.). Values should be obtained in supine as well as dependent leg position because only the combination of these results will yield reliable diagnostic and prognostic clinical information. Critical limb ischemia with poor prognosis should not be assumed if either supine tcpO2 values exceed 10 mmHg or dependent tcpO2 values exceed 45 mmHg.
tcpO2 can be used even in circumstances where conventional hemodynamic evaluation is not feasible.
May contain information that is not supported by performance and intended use claims of Radiometer's products. See also Legal info.
Acute care testing handbook
Get the acute care testing handbook
Your practical guide to critical parameters in acute care testing.
Download nowRelated webinar
Evolution of blood gas testing Part 1
Presented by Ellis Jacobs, PhD, Assoc. Professor of Pathology, NYU School of Medicine.
Watch the webinar